What are the Key Components of a Pneumatic System?

Pneumatic systems play a decisive role in various industries, from manufacturing to transportation. Essentially, they use compressed gas to produce mechanical motion. But what makes up these schemes?
This article will explore the fundamental components of an order and how they operate. Resources like ocpneumatics.com for pneumatics can be invaluable for those venturing deeper into the world of pneumatics.
Compressed Air Generation
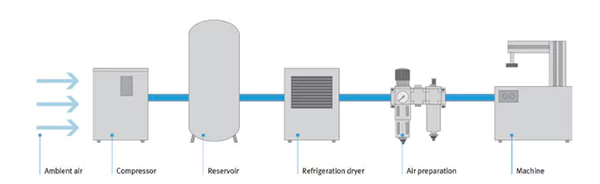
Compressor
The heart of any pneumatic system is the compressor. This device takes in ambient gas, compresses it, and then stores it under high pressure. The compact steam is then used to power various tools or machinery.
Air Reservoir (Tank)
Once the fumes are pressurized, they need to be stored somewhere. This is where the reservoir or tank comes in. It holds the compressed gas until it’s required for use, ensuring a steady supply.
Air Treatment

Air Dryer
Moisture can be detrimental to a pneumatic order. It passes through a vapor dryer to prevent water vapor from causing rust or malfunction. This component removes moisture, ensuring the gas is dry before it’s used.
Did You Know?: A Pneumatic circuit exclusively runs on airpower. Consequently, if the mechanism lacks air rams correctly, the whole process could halt.
Filters
Dust and contaminants can enter the structure during the compression process. Filters help remove these impurities, protecting the system’s components and ensuring its cleanliness.
Control of Compressed Air

Valves
Valves control the flow of condensed fumes. They can be used to start or stop the flow, regulate speed, or direct it to different parts of the arrangement. There are different types of valves, including directional and pressure control valves, each serving a specific function.
Actuators
Actuators are devices that convert the energy from the pressurized gas into mechanical motion. There are two primary types of actuators in this order: cylinders and motors. Cylinders produce linear motion, while motors create rotational motion.
Interesting Fact: Fume cylinders are designed for millions of movements before they wear out.
Pressure Regulators
Pressure regulators are used to ensure that the vapor flows at the right pressure. They adjust the pressure to a level suitable for the task at hand, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Monitoring and Measurement
Pressure Gauges
These tools display the fume pressure levels in various parts of the method. By monitoring these gauges, operators can ensure the network works within the desired pressure range.
Flow Meters
Flow meters measure the rate at which gas flows through the structure. By keeping an eye on the flow rate, one can ensure that the scheme is operating efficiently and detect any potential issues.
Connection and Distribution
Tubes and Hoses
These components transport the compressed air from one part to another. They need to be durable and flexible to handle the pressure and movement within the order.
Fittings and Connectors
For tubes and hoses to function effectively, they need to be securely connected to other components. Fittings and connectors ensure a tight seal, preventing vapor leaks and maintaining the structure’s efficiency.
Safety and Maintenance in Pneumatic Systems

Beyond the fundamental components, safety, and maintenance are paramount in ensuring the longevity and efficiency of this order.
Did You Know?: According to the stats revealed by the British Fluid Power Association, sales of pneumatic equipment have bloomed to over £1.1 billion per annum over the past few years.
Safety Valves
Safety valves, also known as relief valves, play a pivotal role in protecting the system. If the pressure exceeds safe levels, these valves open to release excess gas, preventing potential damages or hazards.
Lubricators
While steam treatment components remove moisture and contaminants, lubricators add controlled amounts of oil to the compact fumes. This lubrication reduces friction in the moving parts of tools and cylinders, ensuring smooth operation and reducing wear.
Maintenance Tools
Routine checks and timely maintenance are necessary for optimum performance. Maintenance tools like wrenches, seal kits, and replacement parts ensure the set-up runs smoothly and extends its lifespan.
Noise Suppressors
High-pressure gas release can generate significant noise, which can harm human ears and cause disturbance in the workspace. Noise suppressors or mufflers are attached to exhaust ports to reduce this noise, making the working environment safer and more comfortable.
Applications of Pneumatic Systems

Pneumatics is everywhere, from powering construction tools to driving industrial machinery. As industries evolve, platforms like ocpneumatics.com for pneumatics become vital in staying updated and sourcing quality components.
Industrial Automation
This method is extensively used in automated assembly lines. They drive machinery and move components and power tools, ensuring rapid and consistent production.
Medical Equipment
From dental chairs to certain surgical tools, pneumatics finds its application in the medical field, offering precision and reliability.
Transportation
Braking schemes in many trains and buses rely on pneumatics. The efficiency and responsiveness of its brakes make them popular in heavy transport.
Construction and Workshop Tools
Pneumatic drills, nail guns, and paint sprayers are just a few tools powered by highly-pressurised fumes. Their power-to-weight ratio and efficiency make them preferred choices in construction sites and workshops.
Wrap-Up
Pneumatic orders have seamlessly integrated into various sectors with their myriad components, proving their versatility and reliability.
While the components are a marvel of engineering, which include the importance of tubes in the Pneumatic system, the real magic lies in how they come together to form schemes that drive our industries, aid in medical procedures, and make transportation safer.
By understanding each component’s role and ensuring its proper maintenance, one can harness the full potential of pneumatics and contribute to smoother, more efficient operations across various domains.










