Comprehensive Strategies for Data Recovery in the Face of Ransomware

Ransomware attacks are increasing, affecting up to 85% of businesses evaluated in 2022.
When some companies chose to pay the ransom, many did not get their data returned, and others became victims of a second attempt.
It can bring a firm to its knees, so you must prepare by implementing strong cybersecurity measures, a complete backup system, and a solid incident response plan.
Businesses should extensively test backup integrity and practice incident response. They must understand how to recover as soon and efficiently as feasible from an event.
Learn more about recommended practices for its protection and how to safeguard your enterprise.
What Is Meant by Ransomware Recovery?
Ransomware is one of the most serious dangers to organizations today.
The number of firms successfully targeted climbed from 76% in 2021 to 85% in 2022, according to the 2023 Data Protection Trends study. Surprisingly, only 55% of encrypted data could be recovered.
Affected businesses lost 45% of their data on average.
There are several varieties of ransomware. Hackers generally lock people out of their workstations and encrypt data to extract large quantities of money.
Moreover, ransomware recovery is a series of purposeful efforts taken by businesses to reduce the effect of attacks.
Organizations develop a system of immutable data backups and configuration snapshots that enable them to reconstruct their systems based on the premise that hackers would successfully encrypt business data.
The efficacy of an organization’s backup and data protection systems and what was impacted during the attack determine the success of ransomware recovery.
Preparing for Ransomware Attacks
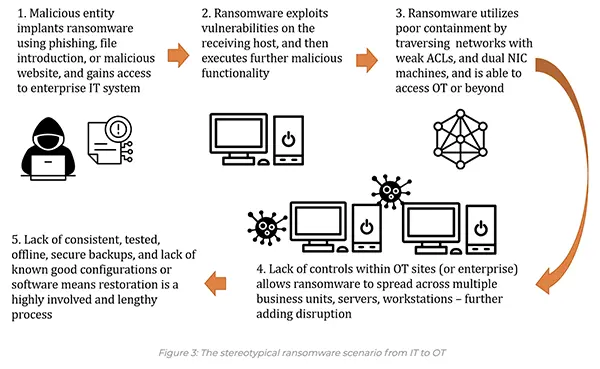
Being ready for ransomware is part of business continuity planning, and the danger of an attack is considerable.
A successful assault might result in serious data loss and the incapacity of your company to operate as a going concern.
Do You Know?:
The Data Breach Investigation Report (DBIR) by Verizon demonstrates that there was a 13% rise in ransomware attacks year-over-year from 2021.
A detailed recovery strategy is required to prepare for an attack. This strategy should be evaluated and properly tested regularly.
It should include best practices for protection, such as robust cybersecurity measures and a thorough backup plan.
Implement Strong Cybersecurity Measures
The first step should be to secure your systems and protect your network against illegal access. The following are vital steps:
- Network security. Keep unauthorized people out of your network. Use strong firewalls to keep hackers out. Segment your network using virtual private networks (VPNs) to limit the scope of a security compromise.
- Patch software. Install software security fixes as soon as possible to reduce the chance of hackers exploiting vulnerabilities.
Interesting Fact:
The first use of ransomware dates back to 1989. It was the time when floppy disks were high-tech and the price of the ransom was a mere $189.
- Email security. Protect user accounts by using sophisticated threat prevention technologies. Users should be educated on email security and how to spot phishing attacks.
- Endpoint protection. Endpoint devices such as laptops, virtual machines (VMs), servers, embedded devices, and mobile devices must all be secured.
Encrypt your data, use multi-factor authentication (MFA), and enforce strong password regulations. Adopt Zero Trust security principles and install endpoint security software.
Make a Comprehensive Backup Plan
Hackers understand the value of backups and deliberately target backup servers.
Create a safe and thorough backup method, and keep these ideas in mind while creating your backup approach.
- 3-2-1-1-0 Rule: This is a development of the traditional 3-2-1 backup strategy. In addition to the original material, it asks for three backups.
Backups should be kept on at least two distinct kinds of media, with one copy offshore and one offline.
The zero in this version of the rule indicates that you should double-check your backups to ensure no mistakes.
- Backup type: Full, incremental, or differential backups may all be part of your plan.
Full backups are often conducted weekly, whereas incremental or differential backups are made daily.
An incremental backup is a second backup that saves any changes since the last full or incremental backup.
A differential accretion is distinct because it backs up all changes since the last complete backup. With each differential backup, its size grows.
- Offsite and cloud-based backups: At least one accretion set should be stored offsite on a distant hardened server or in a secure cloud facility such as Amazon S3 cloud object storage.
- Immutable backups: Backups should be unchangeable. This implies they are read-only and cannot be updated or deleted for a long time.
Immutable backups provide a superior defense.
How to Identify Ransomware Attacks
Early identification of a ransomware infection is crucial since it may avert a full-fledged ransomware assault.

Statistics:
The graph above is about the annual number of ransomware attempts worldwide from 2017 to 2022.
Therefore, organizations all around the world detected 493.33 million ransomware attempts in 2022.
The assault has numerous phases. This comprises initial entrance or infection, reconnaissance and staging, and data encryption, among other things.
If this behavior is detected, you may isolate the impacted computers and reduce the effect of an attack. Here are three ways to consider:
- Monitor and analyze network anomalies. Unexpected network traffic, traffic spikes, restricted network capacity, and unexpected network requests are all indicators of malicious activity.
- Identify ransomware symptoms and indicators. Early signs of an attack may include abnormally high CPU activity and unusually high read and write activity on hard drives.
- Use security information and event management (SIEM) solutions: SIEM software analyzes real-time event log data using machine learning methods to detect risks and suspicious activities.
Best Ransomware Recovery Practices
Despite all the risks, you can recover from an assault. Here are four necessary practices for its recovery that might be the difference between success and failure.
- Test and validate backups: Backups are only useful if they function properly.
Regular validation tests should be done to check for corruption, viruses, or malware. Test backups by mounting them on a VM.
- Prepare a ransomware incident response plan: Have a clear incident response strategy that specifies particular roles.
Make a list of the measures your team needs to follow to recover before an incident occurs.
- Simulate and practice ransomware recovery: Test your strategy by mimicking a ransomware attack.
By employing an offline VM, you may avoid disturbing services. Practice your recovery procedure until everyone is on the same page.
- Train staff on ransomware prevention tactics: Train your employees to spot phishing attempts and other cybercriminal strategies.
What Should You Do After a Ransomware Attack
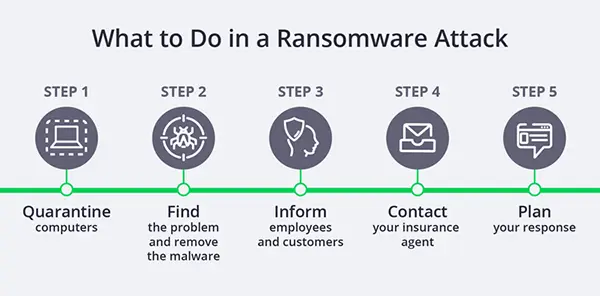
After an attack, and after you’ve recovered, undertake a thorough postmortem analysis to determine what occurred.
- Assess the impact and extent of the ransomware attack: Conduct a post-recovery assessment.
Determine the entire scope of the assault and its consequences of downtime and financial losses.
Determine how the hackers obtained access and if the hackers were successful in compromising your backups.
- Address vulnerabilities: Identify and repair any hardware and software flaws. After that, retrain your personnel.
- Strengthen security: Harden your systems and go over your permissions. Set up more VPNs to further isolate systems. Put MFA practices into action.
- Implement long-term risk mitigation strategies: Connect with cybersecurity groups such as NIST and CISA. Learn how to decrease risk, improve security, and safeguard your systems.
Conclusion
Recovery from ransomware is possible. Paying ransom is not recommended since most firms that pay a ransom only retrieve some of their data.
Proper planning for attacks is necessary for a successful recovery. This involves implementing robust security measures and having a solid backup plan.
A well-coordinated response plan and a well-trained workforce are required; early identification is decisive.
Another consideration is having a solid system that includes several immutable copies. Recognizing the need for ongoing development to respond to changing threats is also important.