What Are Optical Cables, and What Are They Used For?

Over the years, we’ve gotten much better at communicating over long distances. New technology such as radio, telephones, and the Internet have made global communications possible, improving many aspects of our daily lives.
Radio waves and then copper cables were originally used to transmit data, but they have their limitations. Today, most communication networks use optical cables instead.
But what exactly is the technology that is used in these cables? How are they superior to other alternatives, or why are they preferred so much in the market? If you also have the same questions in your mind, read the article till the end.
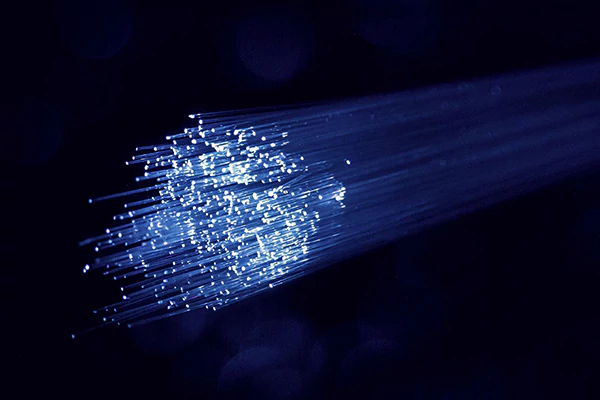
What Are Optical Cables
Optical cables work much in the same way as regular copper ones. They transmit signals along a wire, allowing two devices to interface. This might be used for transmitting audio signals between a source, a receiver, and a speaker. Whereas copper lines send signals using electrons, optical instead send signals in the form of light.
The cable is basically a very thin piece of flexible glass that is protected inside an insulation casing. The advantage of using fiber optics over other cable materials is that light offers higher bandwidth and can share more data over longer distances.
This is especially useful for modern internet network connections, which need to be able to share vast amounts of data as quickly as possible.
DID YOU KNOW?
The first submarine communications cables were laid in the 1850s, establishing the first telecommunications links between continents. The first transatlantic telegraph cable became operational on August 16, 1858.
How Optical Cables Work
Each fiber optic cable contains one or several thin strands of glass. At the center of this strand is a core through which the light travels. Whereas optical cables don’t pose risks of electrocution such as copper lines, they’re still insulated with cladding. This is to protect the cable and also prevent the loss of signal, allowing the light to pass through bends and transfer to the intended destination.
Optical cables use either LED lights or lasers, depending on if they’re single-mode or multi-mode. Each type of cable has different applications, though they both effectively work in the same way. The only difference is that single-mode often transmits light at different wavelengths to combine multiple communication streams in a single pulse of light.
Both methods of transmission are incredibly fast, offering much better speeds than traditional electrical cords. The speed of the data transfer, as well as the range of frequencies that can be used means the bandwidth of the signal is much higher. This makes cords far more efficient and useful for a wide range of purposes.
Uses of Optical Cables
One of the most significant uses of optical cables is in the creation of high-speed internet networks. The internet has changed the world since it first started to gain traction during the 90s. Back then, very few computers had access to the internet, and signals were still sent through copper wires.
This meant slow connections, long loading times, and poor download speeds. They now make up a growing percentage of the broadband infrastructure, providing significantly faster speeds, less interference, and greater bandwidth.
Aside from connecting people all over the world, they can also be used for audio and visual setups. Whereas the majority of audio systems use electronic lines to share data, these threads are a useful alternative.
It’s capable of carrying up to 7.1 channels of high-resolution audio, making it ideal for your surround sound systems and listening to high-fidelity music or enjoying your favorite shows and films.
A wide range of audio file formats are supported by cables, meaning you don’t need to worry about the type of media you’re playing. In most cases, it’s relatively easy to connect up your source to the receiver and speakers, although you may need specialized equipment if you’re dealing with older systems.

INTERESTING FACT
This map shows a picture of optic fiber cables that are spread across the planet, under the sea.
Thankfully, it’s fairly cost-effective, too. Most of them are relatively cheap in price and offer advantages to conventional setups.
Conclusion
You always have a choice in picking an optic fiber cable or a copper cable. However, there are some differences between both of them in their technology, uses, speed, and other specifications. It is significant for you to first identify your needs and then proceed further with a decision.
To summarize, copper cables are a bit slower and more complex than optic fiber cables. To make your functions smoother and streamline data transmission, the optic line must be your go-to choice.