Navigating Paths: The Intersection of Mathematics and Career Guidance

In the digital ecosystem, when automation is taking over various industries, the relevance of mathematics has increased. It has progressed from the mere confines of classrooms to the virtual world, expanding businesses, changing healthcare systems, and transforming the trading world.
Nowadays, being tech-savvy is not just a realm for engineers but holds paramount respect for individuals having analytical skills. The equations and theorems are utilized for problem-solving methodologies, which is an attribute highly sought after in the professional world.
This article will provide a guide or a mentor, leading you to understand the relationship between mathematics and careers related to it. It will also shed light on how a solid foundation in numbers can pave the way for success in various fields.
Mathematics as a Gateway to STEM Careers
A strong foundation in mathematics is necessary to build a career in science, technology, engineering, and STEM. Professions such as computer science, engineering, data analysis, and information technology heavily rely on calculative concepts.
Individuals equipped with numerical skills find themselves at the forefront of innovation, contributing to groundbreaking developments in STEM fields. Another way to empower your journey into the world of STEM careers is with MathMaster, an innovative app designed to assist students in mastering arithmetic concepts.
It ensures they are well-equipped to navigate the challenges in science, technology, engineering, and math. Explore the possibilities with MathMaster at math-master.org.
Actuarial Science: Analyzing Risks and Predicting the Future
Actuaries are professionals who assess financial risks using mathematical and statistical methods. They play a pivotal role in insurance, finance, and pension planning, with a deep understanding of statistics and financial calculations.
They also play a significant role in predicting profitability, making it an attractive professional option for those with a penchant for both numbers and business.
THINGS TO CONSIDER
An actuarial intern is put in a team such as a modeling, testing, valuation, or reinsurance team based on a skill set. By gaining experience as an intern, there are more chances of being hired by big companies.
Data Science and Analytics: Unleashing Insights through Numbers
The surge in big data has given rise to the field of data science, where mathematical modeling and statistical analysis drive decision-making processes.
Data scientists and analysts leverage math algorithms to extract valuable insights from vast datasets. In this way, it influences industries ranging from healthcare to marketing.
Python is the most used programming language by businesses because of its scripting nature that easily automates repetitive tasks. Therefore, training in this program should be prioritized for a long-lasting career in data science.
Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Technology: Securing the Digital Frontier

The rise of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology has created new professional pathways for individuals with a background in math. Cryptographers, blockchain developers, and security analysts employ advanced numerical concepts to create secure and efficient digital ecosystems.
Understanding algorithms and cryptographic principles is paramount in safeguarding the integrity of digital transactions. Though training in this field may seem overwhelming, experts suggest using the task-based approach, identifying questions, and acquiring relatable skills.
Environmental Modeling and Sustainability: Protecting the Planet with Mathematics
Mathematics plays a valuable role in modeling environmental systems, predicting climate patterns, and assessing the impact of human activities on ecosystems. With the growing concerns about improving natural resources, this field is the future for many.
Careers in environmental modeling and sustainability require individuals with calculating skills to analyze complex data sets. They develop models that inform policy decisions aimed at mitigating environmental challenges.
Aerospace Engineering: Navigating the Skies with Precision
Aerospace engineers rely on numerical principles to design and analyze aircraft and spacecraft. From calculating trajectories to ensuring structural integrity, math is an integral component of aerospace engineering.
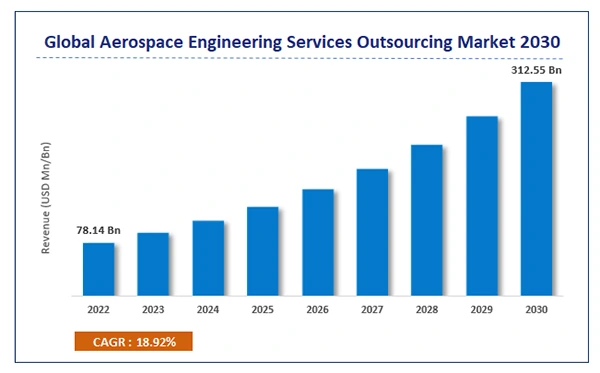
A solid foundation in calculus opens doors to a job where innovation meets exploration in the vast expanse of space. Besides, sectors like manufacturing, aerospace engineers are also in demand in the armed forces and government research agencies.
The graph below shows the salary of an aerospace engineer by 2030. It indicates that this is a high-paying and high-demand job that requires quality training and expertise.
Biostatistics: Bridging Mathematics and Healthcare
In the realm of healthcare, biostatisticians utilize mathematical and statistical methods to analyze medical data, conduct clinical trials, and contribute to advancements in medical research.
These professionals play a necessary role in ensuring that healthcare decisions are based on rigorous statistical evidence, impacting public health and medical breakthroughs. This job has also become relevant as technology helps doctors calculate medical dosages, CAT scans, and X-rays, and predict medical outcomes.
Mathematics in Architecture and Design: Building Beauty and Function
Architects and designers use math principles to create structures that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also structurally sound. The application of geometry, symmetry, and proportion in architectural design showcases the marriage between numbers and creativity.
By using 3D models, designers can define the spatial form of a building accurately and efficiently. It also offers a fulfilling job opportunity for individuals with an eye for both precision and aesthetics.
Financial Analysis and Investment Banking: Decoding Markets with Numbers
The world of finance heavily relies on calculating models and quantitative analysis, with economic analysts, investment bankers, and risk managers leveraging its benefits. They use calculating tools to assess market trends, make informed investment decisions, and manage financial portfolios.
Besides the basic numericals, an investment banking analyst also works with huge spreadsheets where calculations are intricately linked. A solid foundation in numerical skills is a fundamental asset in navigating the complexities of the financial landscape.
Mathematics Education: Nurturing Future Innovators
Beyond traditional career paths, a strong background in calculus and additions opens doors to a rewarding profession in education. Mathematics educators play a pivotal role in shaping the next generation of thinkers, problem solvers, and innovators.
Guiding students through the intricacies of math concepts, educators contribute to the development of a numerically literate society. Understanding new learning software that helps learners to calculate faster, teachers should also include computational methods to further their studies.
Operations Research: Optimizing Efficiency in Business
Operations researchers apply numerical methods to optimize decision-making processes within organizations. The tools that a learner should use in this sector are vector calculus, linear algebra, equations, probability, and computer programming.
From supply chain management to resource allocation, these professionals use number modeling to enhance efficiency and productivity. It also helps them to make significant contributions to the success of businesses and institutions.
Mathematics in Telecommunications: Connecting the World Digitally
The telecommunications industry relies on calculating algorithms for signal processing, data transmission, and network optimization. There are now multiple sources of information online that require computing to process reports and deliver them faster.
Students with skills in math and telecommunication will be most in demand, as people want to hear real stories. Combining the knowledge of cybersecurity is equally beneficial to disperse fake news from the real ones.
Mathematicians and engineers contribute to the development of communication technologies, ensuring seamless connectivity in a progressive, interconnected world.
Mathematics in Art Conservation: Preserving Cultural Heritage with Precision
Art conservators use number techniques for the restoration and preservation of cultural artifacts. It may take a long time to understand and then minimize any replication in terms of context and intent.
Math algorithms aid in analyzing the chemical composition of materials, monitoring environmental conditions, and ensuring the longevity of artworks and historical artifacts. Research in the art restoration field has become comparatively easier with data storage and securing authentic paintings and sculptures.
Urban Planning: Designing Cities for the Future

Urban planners use numerical models to analyze population trends, traffic flow, and resource allocation within cities. In recent times, as the population and traffic in cities grow, mathematical diagrams with technology are being used for better living conditions.
The application of mathematical principles in urban planning contributes to the creation of sustainable and well-designed urban spaces. In this way, urban planners can create less polluted and more environment-friendly living conditions.
Mathematics in Sports Analytics: Decoding Performance Metrics
Sports analytics has become a fast-improving field where mathematicians and statisticians analyze performance metrics to enhance athletic training, strategy, and decision-making.
From player statistics to game simulations, numbers play a vital role in gaining a competitive edge in the world of sports.
Conclusion
The intersection of math and career guidance opens up a myriad of possibilities, showcasing the versatility and applicability of numerical principles across diverse fields.
As technology continues to advance and industries progress, the demand for individuals with strong calculating skills is on the rise.
When contributing to scientific breakthroughs, solving complex real-world problems, or shaping the future of education, individuals equipped with numerical prowess are well-positioned for success in an ever-changing professional landscape.
Also Read: How You Can Make Mathematics Interesting
- Mathematics as a Gateway to STEM Careers
- Actuarial Science: Analyzing Risks and Predicting the Future
- Data Science and Analytics: Unleashing Insights through Numbers
- Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Technology: Securing the Digital Frontier
- Environmental Modeling and Sustainability: Protecting the Planet with Mathematics
- Aerospace Engineering: Navigating the Skies with Precision
- Biostatistics: Bridging Mathematics and Healthcare
- Mathematics in Architecture and Design: Building Beauty and Function
- Financial Analysis and Investment Banking: Decoding Markets with Numbers
- Mathematics Education: Nurturing Future Innovators
- Operations Research: Optimizing Efficiency in Business
- Mathematics in Telecommunications: Connecting the World Digitally
- Mathematics in Art Conservation: Preserving Cultural Heritage with Precision
- Urban Planning: Designing Cities for the Future
- Mathematics in Sports Analytics: Decoding Performance Metrics
- Conclusion